Inhibitors of Bacterial Lectins
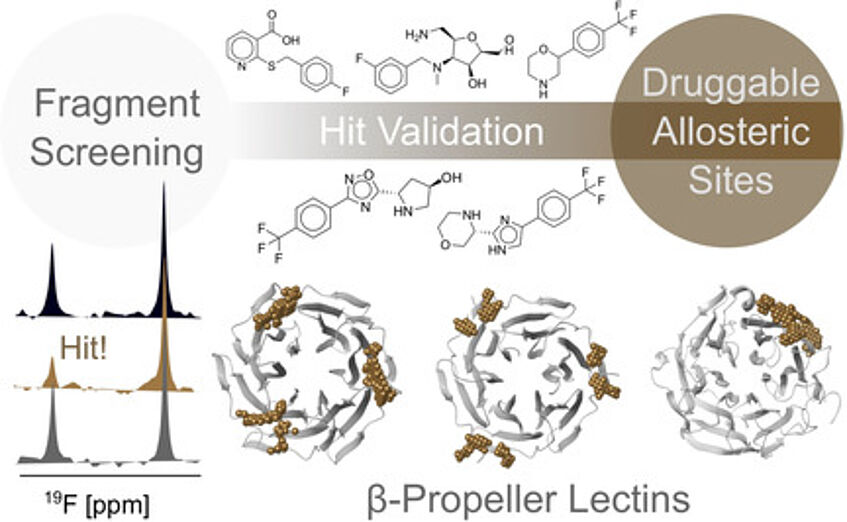
Identification of a druggable pocket in a β-propeller lectin BambL from Burkholderia ambifaria as a potential target for allosteric inhibitors (Shanina et. al, 2021).
Pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites) have developed strategies that utilizes the sugars present on our tissues for recognition, adhesion and infection process. Lectins from the pathogens are located on the capsid of viruses, on pili at the surface of bacteria, or are secreted in the form of toxins and virulence factors. Molecules that could interfere with such carbohydrate-protein interactions are therefore of high interest as anti-infectious agents. Since they prevent the binding without killing the pathogens, they have different modes of action than antibiotics and could be of great interest for the arising issues of multiresistant pathogens. We have applied a variety of biophysical approaches to identify new inhibitors for bacterial lectins and have also explored the possibility for allosteric modulation of these targets.
Further reading
Shanina, E.; Kuhaudomlarp, S.; Lal, K.; Seeberger, P. H.; Imberty, A.; Rademacher, C.
Druggable Allosteric Sites in Β-Propeller Lectins.
Angewandte Chemie Int Ed 2022, 61 (1), e202109339.
Siebs, E.; Shanina, E.; Kuhaudomlarp, S.; Gomes, P. S. F. C.; Fortin, C.; Seeberger, P. H.; Rognan, D.; Rademacher, C.; Imberty, A.; Titz, A.
Targeting the Central Pocket of the Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Lectin LecA.
Chembiochem 2022, 23 (3), e202100563.
Kuhaudomlarp, S.; Siebs, E.; Shanina, E.; Topin, J.; Joachim, I.; Gomes, P. S. F. C.; Varrot, A.; Rognan, D.; Rademacher, C.; Imberty, A.; Titz, A.
Non-Carbohydrate Glycomimetics as Inhibitors of Calcium(II)-Binding Lectins.
Angew Chem-ger Edit 2021, 133 (15), 8185–8195.
Shanina, E.; Siebs, E.; Zhang, H.; Silva, D. V.; Joachim, I.; Titz, A.; Rademacher, C.
Protein-Observed 19F NMR of LecA from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa.
Glycobiology 2020, 31 (2), 159–165.
